Essential Computer Hardware
A computer’s hardware devices fall into one of four categories
- Processor
- Memory
- Input and Output
- Storage
Processor
The procedure that transforms raw data into useful information is called processing. To perform this transformation, the computer makes use of two components; the processor and memory. The processor in personal computers consists of one or more specialized chips called microprocessor. A microprocessor is plugged into the computer’s motherboard. The motherboard is a rigid rectangular panel containing the circuitry that connects the processor to other hardware components. The motherboard is a typical example of a circuit board. In most personal computers many internal devices such as video cards, sound cards, disk controllers and other devices are housed on their own smaller circuit boards which attach to the motherboard. In many newer computers, these devices are directly into the motherboard. Nowadays, some microprocessors are large and complex enough to require their own dedicated circuit boards which plug into a special slot in the motherboard. The motherboard can be thought of as the master circuit board in a computer.
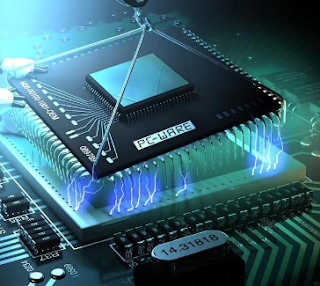 |
| A CPU fits into its slot on the motherboard |
Microprocessors are silvers of silicon or other material etched with many tiny electronic circuits. To process data or complete an instruction from a user or a program, the computer passes electricity through the circuits. A personal computer’s processor is usually a single chip or a set of chips contained on a circuit board. In some powerful computers, the processor consists of many chips and the circuit boards on they are mounted. In either case the term central processing unit (CPU) refers to a computer’s processor. Many at times people refer to computer system by the type of CPU they contain.
Memory Devices
A memory is one or more set of chips that data or program instructions either permanently or temporarily. Memory is a critical processing component in any computer. Personal computers use several different types of memory, but the two most important are called random access memory (
RAM) and read-only memory (
ROM). These two types of memory work in very different ways and perform distinct functions.
Random Access Memory
The most common type of memory is called random access memory (
RAM). Because of this the term memory is used to refer to RAM. The RAM is like an electronic scratch pad inside the computer. It holds data and program instructions while the CPU works with them. When a program is launched, it is loaded into and run from memory. As the program needs data, it is loaded into memory for fast access. Data entered into the computer is stored in the memory but only temporarily. Data is both written to and read from this memory. Because of this RAM is sometimes referred to as
read/write memory. Similar to many other computer components, the RAM is made up a set of chips mounted on a circuit board.
RAM is
volatile which means it loses its content when the computer goes off or shuts down or when there is power failure. It is therefore required for RAM to be continuously supplied with power to hold its data. For this reason you should save your data files to a storage device frequently to avoid losing them when there is power failure.
RAM has tremendous impact on the speed and power of a computer. Generally, the more the RAM, the faster the computer can quickly perform tasks. The most common measurement unit for describing a computer’s memory is the
byte, which is the amount of memory it takes to store a single character such as a letter or a numeral. Many computers nowadays have higher memory with at least 512MB to over 24GB.
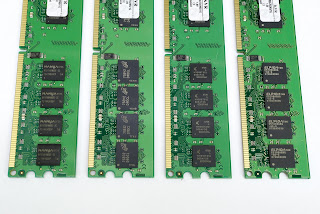 |
| RAM of a computer |
Read-Only Memory
Unlike RAM, the read-only memory (ROM) stores its data permanently even when the computer shuts off. ROM is called
non-volatile memory because it doesn’t lose its content. ROM holds instructions the computer needs to operate. When the computer is booted, it checks and retrieves data from the ROM for features that enable it to start up and information about its hardware devices.
 |
| ROM of a computer |
Input and Output Devices
A personal computer would be useless if you could not interact it because the machine could not receive its instructions or deliver the results of its work.
Input devices accept data and instructions from the user or from another computer system (such as a computer on the internet).
Output devices return processed data to the user or to another computer system.
The most common input device is the keyboard, which accepts numbers, letters and commands from the user. Another important type of input device is the mouse which lets you select options from on-screen menus. You use a mouse by moving it across a flat surface and pressing its buttons. There are a variety of input device that work with personal computers too. These include;
A trackball and touch-pad are variations of the mouse and enable you to draw or point on the screen.
 |
| Touch-pad of a laptop |
|
|
 |
| Trackball of a mouse |
|
The
joystick is a swiveling lever mounted on a stationary base that is well suited for playing video games.
 |
| Game controller Joysticks |
A
scanner can copy a printed page of text or graphic into the computer’s memory, freeing you from creating the data from scratch.
 |
| Scanner |
A
digital camera can record still images, which you can view and edit on the computer.
 |
| Nikon digital camera |
A
microphone enables you to input your voice or music as data.
 |
| A microphone |
The function of an
output device is to present processed data to the user. The most common output devices are the
monitor and the
printer. The computer sends output to the monitor which is the display screen only when the user needs to see the output. It sends output to the printer when the user requests a paper copy often referred to as a hard-copy of a document.
 |
| Computer monitor |
|
 |
| A printer |
|
Just as computers can accept sound as input, they can use
stereo speakers or
headphones as output devices to produce sound. Some types of hardware can act as both input and output devices. A touch screen for example is a type of monitor that displays text or icons you can touch. When the screen is touched, special sensors detect the touch and the computer calculate the point on the screen where you placed a finger. Depending on the location of the touch, the computer determines what information to display or what action to take next.
 |
| Stereo speakers |
|
 |
| Headphone |
|
Communication devices are the most common types of devices that can perform both input and output. These devices connect one computer to another in a process known as
networking. The most common kinds of communication devices are
modems, which enable computers to communicate through telephone lines or cable television systems and Network Interface Cards (NICs), which let users connect a group of computers to share data and devices.
 |
| Belkin modem |
Storage Devices
A computer can function with only processing, memory, input and output devices. To be useful however, a computer needs a place to keep program files and related data when they are not in use. The main purpose of storage is to hold data permanently even when the computer is turned off.
You may think of storage as an electronic file cabinet and RAM as an electronic worktable. When you need to work with a set of data or program, the computer locates it in the file cabinet and puts a copy on the table. After you have finished working with the data or program, you put it back into the file cabinet. The changes you make to the data while working on it replace the original file in the cabinet (unless you store it in a different place).
Novice computer users often confuse storage with memory. Although the functions of storage and memory are similar, they work in different ways. There are three major differences between storage and memory.
- There is more room in storage than in memory, just as there is more room in a file cabinet than there is on a tabletop.
- Contents are retained in storage when the computer is turned off, whereas programs or data in memory disappear when the computer is shut down.
- Storage devices operate much slower than memory chips, but storage is much slower than memory.
There are two main types of computer storage: magnetic and optical.
Magnetic Storage
There are many types of computer storage, but the most common is the
magnetic device. A
disk is a round, flat object that spins around its center. Magnetic disk almost always housed inside a case of a kind so the disk itself cannot be seen unless the case is opened.
Read/write heads which work in much the same way as the heads of a tape recorder or VCR are used to read data from the disk or write data onto the disk.
 |
| Hard disk parts |
The device that hold the disk is called a
disk drive. Some disks are built into the drive and are not meant to be removed. Other kinds of drives allow for removal and replacement of disks. Most personal computers have at least one non-removable hard disk or disk drive. In addition, there is also a
diskette drive, which allows you to use removable diskettes or floppy disks. The hard disks serves as the computer’s primary filing cabinet because it can store more data than a diskette can contain. Diskettes are used to load data onto the hard disk, to trade data with other users and to make backup copies of the data on the hard disk.
Optical Storage
Nearly all computers sold today include at least one form of optical storage.
Optical storage are devices that use lasers to read data from or write data to the reflective surface of an optical disc.
The
CD-ROM is the most common type of optical storage device. Compact disks (CDs) are a type of optical storage, identical to audio CDs. Until recently a standard CD could store about 74 minutes of audio or 650MB of data. A newer breed of CDs can hold 80 minutes of audio or 700MB of data. The type used in computers is called Compact Disk Read-Only Memory (CD-ROM). As the name implies you cannot change the information on the disk, just as an audio CD cannot be recorded over.
 |
| CD-Rom |
If you purchase a
CD-Recordable (CD-R) drive, you have the option of creating your own CDs. A CD-R drive can write data to and read data from a compact disc. To record data with a CD-R drive, you must use a special CD-R disk which can be written on only once or a
CD-Rewritable (CD-RW) disc, which can be written to multiple times like a floppy disk.
An increasingly popular data storage technology is the
Digital Video Disc, which is revolutionizing home entertainment. Using sophisticated compression technologies, a single DVD which is similar in size to a standard compact disc can store an entire full-length movie. DVDs can hold a minimum of 4.7GB of data and as much as 17GB. Future DVD technology promise much high storage capacities on a single disc. DVD drives can locate data on disc much faster than CD-ROM drives.
 |
| DVD ROM |
DVDs require special player, however many DVD players can play audio, data and DVD discs, freeing the user from purchasing players for each type of disc. DVD drives are now standard equipment on many new personal computers. Users not only can install program and data from their standard CD, but they can also watch movies on their personal computers using a DVD.





















































